Archive:ODROID: Difference between revisions
Gamester17 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(Included some more detailed install instructions.) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:ODROID-X.jpg|400px|right]] | [[File:ODROID-X.jpg|400px|right]] | ||
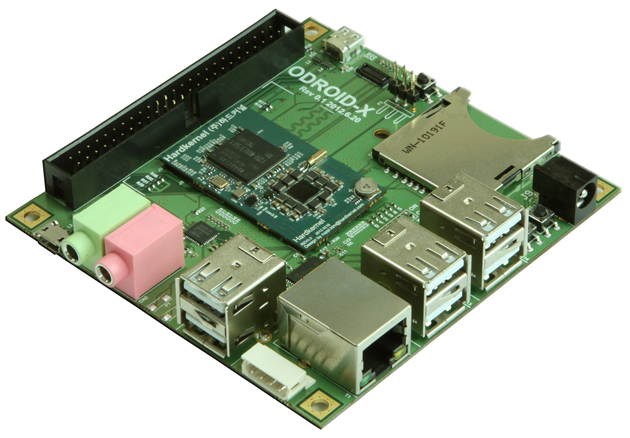
<section begin="intro" />'''ODROID | <section begin="intro" />'''ODROID''' is a series of powerful ARM-based single-board computers (developer boards), manufactured by Hardkernel Co., Ltd., an open-source hardware company located in South Korea, capable of running Android or Linux. {{Kodi}} has been ported for use on Hardkernel ODROID-X, X2, U2, U3, XU, XU2, XU3 and XU3 Lite. As an Kodi HTPC, the ODROID-C series supports Full 1080p (Full HD) video playback of the most commonly used codecs, support for most if not all Kodi [[add-ons]], and offers adequate GUI performance.<section end="intro" /> | ||
The ODROID | The ODROID series was primary designed to act as a development platform for developers wanting to prototype embedded systems based on Samsung Exynos 3, 4, and 5 series of System-on-Chips (SoC), but have since also been made popular for multi-purpose use by low-power device enthusiasts and hobbyist alike, including those using it for as HTPC (Home Theater PC) for {{Kodi}}. | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Even though the product name ‘ODROID’ is a portmanteau of ‘open’ + ‘Android’, the hardware isn't actually fully open source because some parts of the design are retained proprietary by the company. | Even though the product name ‘ODROID’ is a portmanteau of ‘open’ + ‘Android’, the hardware isn't actually fully open source because some parts of the design are retained proprietary by the company. As a home media center this line of boards offers a very cheap HTPC Client that works far better then similar devices like the rPi. | ||
== Installing {{Kodi}} == | == Installing {{Kodi}} (OpenELEC) == | ||
* | The best option for {{Kodi}} is to use openelec. However the official Ubuntu image from HardKernel also includes a modified version of kodi (Often outdated and can not be updated). | ||
* | |||
Installation is pretty simple for the Openelec Builds. (Windows): | |||
* Download Win32 Disk Imager: http://com.odroid.com/sigong/blog/blog_list.php?bid=144 (Download link is below the image.) | |||
* Download The disk image for your odroid: | |||
** For the C1 or C1+ use the latest image from here: http://forum.odroid.com/viewtopic.php?f=114&t=16093 (Latest version at the top may be a Beta. You must download a SD card image. Then you can update to a later version if the version you want does not have an image.) | |||
** For all other version use one from here: from here: http://forum.odroid.com/viewtopic.php?f=79&t=5915 (Scroll past the sources to the Images.) | |||
* Insert your SD card or eMMC and start the Win32 Disk Imager. | |||
* Select your disk Image and the drive letter and click Write. Once the process is complete Click Verify. If the verification fails Click write again and the verify again. If it still fails ignore it. | |||
* Insert the SD or eMMC into your odroid, plug your HDMI and Wifi module in before you plug the power in. | |||
* The Odroid will start and show the Openelec Logo for a few minuets. The Odroid will then restart and Boot into Kodi. You will be greeted with the OpenELEC startup screen. Follow the prompts and you will be enjoying in no time. | |||
* Ubuntu-based - Head to the wiki page for your board for the current Ubunut image. http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php | |||
* Android - [[HOW-TO:Install Kodi for Android]] | * Android - [[HOW-TO:Install Kodi for Android]] | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 7 January 2016
| These pages are maintained by the community and should not be considered an endorsement or recommendation. Device pages are made when there's a bunch of useful information for a particular device, and someone takes the time to make that page. Keep in mind, some devices simply don't need a page of specific information, but are still excellent devices. * |
ODROID is a series of powerful ARM-based single-board computers (developer boards), manufactured by Hardkernel Co., Ltd., an open-source hardware company located in South Korea, capable of running Android or Linux. Kodi has been ported for use on Hardkernel ODROID-X, X2, U2, U3, XU, XU2, XU3 and XU3 Lite. As an Kodi HTPC, the ODROID-C series supports Full 1080p (Full HD) video playback of the most commonly used codecs, support for most if not all Kodi add-ons, and offers adequate GUI performance.
The ODROID series was primary designed to act as a development platform for developers wanting to prototype embedded systems based on Samsung Exynos 3, 4, and 5 series of System-on-Chips (SoC), but have since also been made popular for multi-purpose use by low-power device enthusiasts and hobbyist alike, including those using it for as HTPC (Home Theater PC) for Kodi.
Overview
Even though the product name ‘ODROID’ is a portmanteau of ‘open’ + ‘Android’, the hardware isn't actually fully open source because some parts of the design are retained proprietary by the company. As a home media center this line of boards offers a very cheap HTPC Client that works far better then similar devices like the rPi.
Installing Kodi (OpenELEC)
The best option for Kodi is to use openelec. However the official Ubuntu image from HardKernel also includes a modified version of kodi (Often outdated and can not be updated).
Installation is pretty simple for the Openelec Builds. (Windows):
- Download Win32 Disk Imager: http://com.odroid.com/sigong/blog/blog_list.php?bid=144 (Download link is below the image.)
- Download The disk image for your odroid:
- For the C1 or C1+ use the latest image from here: http://forum.odroid.com/viewtopic.php?f=114&t=16093 (Latest version at the top may be a Beta. You must download a SD card image. Then you can update to a later version if the version you want does not have an image.)
- For all other version use one from here: from here: http://forum.odroid.com/viewtopic.php?f=79&t=5915 (Scroll past the sources to the Images.)
- Insert your SD card or eMMC and start the Win32 Disk Imager.
- Select your disk Image and the drive letter and click Write. Once the process is complete Click Verify. If the verification fails Click write again and the verify again. If it still fails ignore it.
- Insert the SD or eMMC into your odroid, plug your HDMI and Wifi module in before you plug the power in.
- The Odroid will start and show the Openelec Logo for a few minuets. The Odroid will then restart and Boot into Kodi. You will be greeted with the OpenELEC startup screen. Follow the prompts and you will be enjoying in no time.
- Ubuntu-based - Head to the wiki page for your board for the current Ubunut image. http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php
- Android - HOW-TO:Install Kodi for Android
See also
- Android hardware - Other Android platform which Kodi supports hardware video decoding on.
- Android - Android operating system information in regards to Kodi usage.
Links
- Hardkernel ODROID website - http://hardkernel.com