Raspberry Pi: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
<section end="performance" /> | <section end="performance" /> | ||
== | == Remote controls == | ||
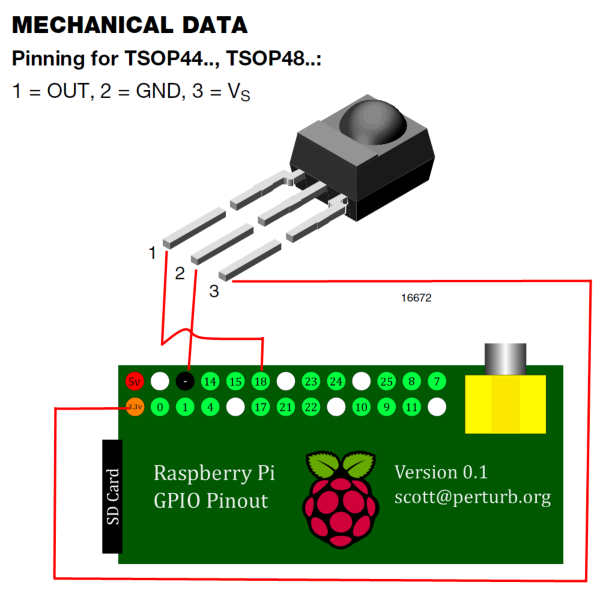
[[File:gpioir.png|right|300px|thumb|Wiring instructions for a TSOP4838 GPIO IR sensor.]] | |||
;GPIO IR receiver | |||
:Don't have a CEC TV or a smartphone remote? For less than a dollar/euro, you can add an IR receiver to your Raspberry Pi that works with most MCE and Apple remotes (and a few others). Most {{kodi}} install options for the Pi should work with the GPIO IR out of the box, or by enabling a setting from within {{kodi}}. Go to a local electronics store or search on ebay for "<code>TSOP4838</code>" and use some simple jumper wires (or solder the pins directly, if you wish). | |||
;[[CEC]] | |||
:If your TV supports '''[[CEC]]''' then you should be able to use the remote control that came with your TV to control {{kodi}}. The remote control signals are sent over the HDMI cable and most often don't require any further settings or configuration. | |||
;[[MCE remotes]] | |||
{{-}} | |||
== How good is it, really? == | == How good is it, really? == | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 18 October 2014
| For more info and help, check out the XBMC Raspberry Pi support forum |
The Raspberry Pi is an ARM powered, credit card sized computer developed in the UK by the Raspberry Pi Foundation for educational and hobbyist purposes. The low power computer is mass produced at very low prices and the high number of units sold gives it massive community support. As an XBMC HTPC, the Pi supports full 1080P video playback, supports most major codecs, most if not all XBMC add-ons, and a reasonably responsive GUI.
Installing XBMC
The easiest way to install XBMC on an R-Pi is to use one of these pre-made OS/XBMC packages:
- OpenELEC - Installing • FAQ • Help forum • USB drive install
- Raspbmc - Installing: Windows, Mac OS X, Linux • FAQ • User guide - Help forum
- XBian - Installing • FAQ • Starters guide • Forum
- Which one do I install?
If you just need Kodi, which is how you will get the best performance out of the Pi, then install OpenELEC.
If you need to install additional programs along side Kodi then look at Raspbmc. Keep in mind that OpenELEC includes OE add-ons for most common programs, like download clients, file sharing, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
- See: Raspberry Pi FAQ
Maximizing performance
- Install OpenELEC.
- Use a lightweight skin such as the default Confluence, Amber, Quartz, Bellow, or xTV-SAF.
- Turn off RSS feeds and any scrolling text options for your skin.
- Use an SD card with good rewrite speeds. The class of the SD card doesn't always mean it will be faster, as that speed listing is for sustained reading and writing. For Kodi random read/write speeds are more important. The class 4/6 Samsung SD cards sold on the Raspberry Pi Store (the ones with NOOBS on them) typically have much better performance than most class 10 cards. For more information about SD card speeds, check out this excellent thread on the R-Pi forum: http://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?p=53159
- You can also try to use a combination of SD and fast USB drive for your Kodi install, but recent improvements to the software make it so that even just using a good SD card is about as fast as using a fast USB drive.
- Avoid using wifi. If you do use wifi, use a wifi adapter that contains two antenna (either internally or externally). Otherwise, stick to wired ethernet, local USB drives, or ethernet-over-power devices (like Homeplug, etc).
- If you are using wifi and it seems just on the edge of being fast enough, check out HOW-TO:Modify the video cache.
- Try using NFS file shares instead of SMB file shares.
- Overclock. Most (but not all) Pi's can be overclocked to some point, as long as they have a good power supply. All Raspberry Pi's are clocked at a speed that will work by default, but when the CPUs are made they can sometimes handle a faster speed without crashing. This depends on each individual unit, and there's no universal setting that will work for everyone (except for the default speed that you get without overclocking). Try various overclocking settings and run Kodi for a while and see if it's stable. If one group of overclocking settings causes crashes, try a group of settings that are lower than that. For more information about this check out this forum thread: http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?tid=199272
- Disable "Extract thumbnail and video information" from file lists settings for faster menus
- For smoother video playback enable "Adjust display refresh rate to match video" from playback settings
- Make sure the video is using H.264 (up to High Profile. Hi10P will not work) or MPEG-4, or, if a codec was purchased and enabled, MPEG-2 or VC-1.
- Passthrough is recommended as it lowers CPU usage for DTS and AC3. Use audio passthrough if your TV/receiver supports it.
- To determine which audio passthrough formats your HDMI-connected TV supports, you can log in to your chosen distribution, via SSH, and run this command:
/opt/vc/bin/tvservice a(on OpenELEC:tvservice -a).
- Feeling adventurous? Check out the latest OpenELEC test builds, which often have even more speed improvements. Just remember that these builds can often be unstable: http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?tid=192380
Remote controls
- GPIO IR receiver
- Don't have a CEC TV or a smartphone remote? For less than a dollar/euro, you can add an IR receiver to your Raspberry Pi that works with most MCE and Apple remotes (and a few others). Most Kodi install options for the Pi should work with the GPIO IR out of the box, or by enabling a setting from within Kodi. Go to a local electronics store or search on ebay for "
TSOP4838" and use some simple jumper wires (or solder the pins directly, if you wish).
- CEC
- If your TV supports CEC then you should be able to use the remote control that came with your TV to control Kodi. The remote control signals are sent over the HDMI cable and most often don't require any further settings or configuration.
How good is it, really?
See for yourself: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ErWF2sYgJec
Further reading
Random notes
Feel free to place various notes, tips, and links here. As this section of the wiki gets more organized, those notes will be properly sorted. Consider this like a dumping ground for when you're not sure where to put something.