Raspberry Pi: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
! Model B | ! Model B | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Target price: | | Target price:<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| | | $25 | ||
| | | $35<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/news/9112841/Mini-Raspberry-Pi-computer-goes-on-sale-for-22.html | location=London | work=The Daily Telegraph | first=Donna | last=Bowater | title=Mini Raspberry Pi computer goes on sale for £22 | date=29 February 2012}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| SoC: | | [[System-on-a-chip|SoC]]:<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| colspan="2" | Broadcom BCM2835 (CPU | | colspan="2" | [[Broadcom]] BCM2835 (CPU, GPU, DSP, and SDRAM)<ref name="Broadcom-BCM2835-Website">[http://www.broadcom.com/products/BCM2835 BCM2835 Media Processor; Broadcom.]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CPU: | | CPU: | ||
| colspan="2" | 700 MHz ARM1176JZF-S core (ARM11 family) | | colspan="2" | 700 MHz ARM1176JZF-S core ([[ARM11]] family)<ref name="Broadcom-BCM2835-Website"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| GPU: | | GPU: | ||
| colspan="2" | Broadcom VideoCore IV, OpenGL ES 2.0, | | colspan="2" | Broadcom [[VideoCore]] IV,<ref name="hq-qa"> | ||
{{cite web | |||
| title = Q&A with our hardware team | |||
| publisher = Raspberry Pi Foundation | |||
| url = http://www.raspberrypi.org/2011/09/qa-with-our-hardware-team/ | |||
| accessdate =20 September 2011 | |||
}}</ref> [[OpenGL ES]] 2.0, [[1080p]]30 [[h.264/MPEG-4 AVC]] high-profile decoder<ref name="Broadcom-BCM2835-Website"/> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Memory (SDRAM): | | Memory (SDRAM): | ||
| colspan="2" | 256 | | colspan="2" |256 Megabytes (shared with GPU) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| USB 2.0 ports: | | USB 2.0 ports:<ref name="VerifiedPeripheralList">[http://elinux.org/RaspberryPiBoardVerifiedPeripherals Verified USB Peripherals and SDHC Cards; eLinux.org]</ref> | ||
| 1 | | 1 | ||
| 2 (via integrated USB hub) | | 2 (via integrated USB hub)<ref name="SMSC-LAN9512-Website">[http://www.smsc.com/index.php?tid=300&pid=135 SMSC LAN9512 Website; smsc.com]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Video outputs: | | Video outputs:<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| colspan="2" | Composite RCA, HDMI | | colspan="2" | [[Composite video|Composite RCA]] (PAL & NTSC), [[HDMI]] (rev 1.3 & 1.4) <ref name=quickguide>[http://elinux.org/RPi_Hardware_Basic_Setup Embedded Linux Wiki: Hardware Basic Setup]</ref>, raw [[Liquid crystal display|LCD]] Panels via [[Display Serial Interface|DSI]] <ref name="DSI">[http://elinux.org/Rpi_Screens Raspberry Pi Wiki, section screens]</ref><ref>[http://elinux.org/File:Raspi-Model-AB-Mono-2-699x1024.png diagram of Raspberry Pi with DSI LCD connector]</ref> | ||
14 HDMI resolutions from 640×350 to 1920×1200 plus various [[PAL]] and [[NTSC]] standards.<ref name="video">[http://www.raspberrypi.org/forum/general-discussion/config-txt/page-3 Raspberry Pi, supported video resolutions]</ref> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Audio outputs: | | Audio outputs:<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| colspan="2" | 3.5 mm jack, HDMI | | colspan="2" | [[TRS connector|3.5 mm jack]], HDMI | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Onboard storage: | | Onboard storage:<ref name="VerifiedPeripheralList"/> | ||
| colspan="2" | SD / MMC / SDIO card slot | | colspan="2" | [[Secure Digital|SD]] / [[MultiMediaCard|MMC]] / SDIO card slot | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Onboard network: | | Onboard network:<ref name="faq" /><ref name="VerifiedPeripheralList"/> | ||
| None | |||
| 10/100 Ethernet | | 10/100 [[Ethernet]] ([[Registered jack#RJ45|RJ45]])<ref name="SMSC-LAN9512-Website"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Low-level peripherals: | | Low-level peripherals: | ||
| colspan="2" | 8 | | colspan="2" | 8 × [[General Purpose Input/Output|GPIO]], [[Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter|UART]], [[I²C]] bus, [[Serial Peripheral Interface Bus|SPI]] bus with two [[chip select]]s, +3.3 V, +5 V, ground<ref name="hq-qa" /><ref>[http://elinux.org/RPi_Low-level_peripherals Raspberry Pi GPIO Connector; eLinux.org]</ref><br/>'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Power ratings: | | Power ratings: | ||
| 500 mA (2.5 W) | | 500 mA (2.5 [[Watt|W]])<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| 700 mA (3.5 W) | | 700 mA (3.5 W) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Power source: | | Power source:<ref name="faq" /> | ||
| colspan="2" | 5 volt via MicroUSB or | | colspan="2" | 5 [[volt]] via [[USB#Mini and Micro connectors|MicroUSB]] or GPIO header | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Size: | | Size: | ||
| colspan="2" | 85.60 × 53.98 mm | | colspan="2" | {{convert|85.60|×|53.98|mm|in|abbr=on}}<ref>[http://www.raspberrypi.org/archives/344 Final PCB artwork]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Planned operating systems: | ||
| colspan="2" | | | colspan="2" | [[Debian|Debian GNU/Linux]], [[Fedora (operating system)|Fedora]], [[Arch Linux]]<ref name="raspberrypi faqs"> | ||
{{cite web | |||
| url=http://www.raspberrypi.org/faqs | |||
| title=FAQs | |||
| publisher=Raspberry Pi | |||
| accessdate=3 November 2011 | |||
}}</ref>, [[RISC OS]] <ref name="osnews risc os" /> | |||
|} | |} | ||
;Notes: | |||
# '''Model A''' and '''Model B''' are cultural references<ref name="raspberrypi model names">{{cite web | url=http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/11/28/raspberry_pi/page3.html | title=Psst, kid... Wanna learn how to hack? | publisher=The Register | date=28 November 2011 | accessdate=24 December 2011 | author=Williams, Chris}}</ref> to the original models of the British educational [[BBC Micro]] computer, developed by [[Acorn Computers]], who originally developed the [[ARM]] processors (the architecture of the Raspberry Pi) and operating system [[RISC OS]], which will also be able to be run on the Raspberry Pi (version 5.17).<ref name="osnews risc os" /> | |||
# On the model B beta boards, 128 MB was allocated by default to the GPU, leaving 128 MB for the CPU.<ref> [http://www.reddit.com/r/raspberry_pi/comments/oicyr/i_have_a_raspberry_pi_beta_board_ama/c3hj3n0 I have a raspberry pi beta board ama] </ref> On the release model B (and Model A) three different splits are possible: 192 MB (CPU RAM) is the default split. It should be sufficent for standalone 1080p video decoding, or simple 3D (but probably not both together). 224 MB is for Linux only, with just a 1080p framebuffer; likely to fail for any video or 3D. 128 MB is for heavy 3D, possibly also with video decoding (e.g. XBMC).<ref>[http://www.raspberrypi.org/forum/general-discussion/config-txt/page-3 Raspberry Pi boot configuration text file]</ref> Comparatively the Nokia 701 uses 128 MB for the Broadcom VideoCore IV.<ref> [http://www.raspberrypi.org/forum/general-discussion/nokia-701-has-a-similar-broadcom-gpu Nokia 701 has a similar Broadcom GPU] </ref> | |||
# Level 2 Cache is 128 KB, used primarily by the GPU, not the CPU. | |||
# The [[ARM11]] is based on version 6 of the [[ARM architecture]], which due to its age is no longer supported by several popular versions of Linux, including Ubuntu. | |||
# The available memory, 128–224 MiB, after subtracting 32–128 MiB for graphics memory, is less than the stated minimum requirement of 768 MiB to run a standard build of the Fedora operating system.<ref> [http://fedoraproject.org/get-fedora Fedora, What will I need?]</ref> Neither the memory nor processing power meets the Debian recommended minimums, even for systems without a desktop. However, 128 MiB meets the absolute minimum for an i386 system, even with a desktop. The Debian manual states: "most users risk being frustrated if they ignore these suggestions."<ref>[http://www.debian.org/releases/stable/i386/ch03s04.html.en Debian Minimum Hardware Requirements ''(Retrieved 16 February 2012)'']</ref> | |||
# The 128–224 MiB of available memory is twice the minimum requirement of 64 MiB needed to run [[Slackware Linux]] on an ARM or i386 system.<ref>[http://www.slackware.com/install/sysreq.php The Slackware Linux Project: Installation Help<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> There are reports of Slackware running well on 32 MB ARM<ref>[http://lists.armedslack.org/pipermail/armedslack/2010-March/thread.html#356 The ARMedslack March 2010 Archive by thread<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> and i386<ref>[http://www.slackbook.org/html/book.html#INSTALLATION-REQUIREMENTS Slackware Linux Essentials<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> systems. (While Slackware can load and run a GUI, it was designed to be run from the [[Shell (computing)|shell]].) The [[Fluxbox]] window manager running under [[X Windows]] requires an additional 48 MB of RAM<ref>[http://linuxreviews.org/software/desktops/#toc4 Desktops: KDE vs Gnome (Linux Reviews)<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> (112 MB total). | |||
# the Raspberry Pi (model B) also contains a 15-pin [[Mobile Industry Processor Interface|MIPI]] [[Camera interface]] (CSI) connector, which at the moment is unsupported, but the foundation is planning to release a camera module for it, sometime in the near future.<ref>[http://www.raspberrypi.org/forum/features-and-requests/camera-for-the-csi-2-port camera for the CSI-2 port]</ref><ref>[http://elinux.org/File:Raspi-Model-AB-Mono-2-699x1024.png diagram of Raspberry Pi with CSI camera connector]</ref> | |||
# Support for Raw [[liquid crystal display|LCD]] Panels is available in hardware through the available DSI connector from the [[Mobile Industry Processor Interface]] (MIPI®) Alliance. <ref name="DSI" /> Software support is being planned. | |||
# Supported digital video resolutions are: 640x350 [[Enhanced Graphics Adapter|EGA]]; 640x480 [[Video Graphics Array|VGA]]; 800x600 [[Super video graphics array|SVGA]]; 1024x768 [[XGA]]; 1280×720 [[720p]] [[High-definition television#High-definition display resolutions|HDTV]]; 1280x768 [[Graphic display resolutions#WXGA|WXGA]] Variant; 1280x800 [[Graphic display resolutions#WXGA|WXGA]] Variant; 1280x1024 [[SXGA]]; 1366x768 [[Graphic display resolutions#WXGA|WXGA]] Variant; 1400x1050 [[SXGA+]]; 600x1200 [[UXGA]]; 1680x1050 [[WXGA+]]; 1920x1080 [[1080p]] [[High-definition television#High-definition display resolutions|HDTV]]; 1920x1200 [[WUXGA]].<ref name="video" /> Also to be supported are the generation of [[576i]] and [[480i]] composite video signals for [[Pal#PAL-B.2FG.2FD.2FK.2FI|PAL-BGHID]], [[PAL-M]], [[PAL-N]], [[NTSC]] and [[NTSC-J]] <ref name="composite">[http://www.raspberrypi.org/forum/general-discussion/pictures-of-screen-displaying-example-of-rpi-composite-output?value=480i&type=1&include=2&search=1 examples of Raspberry Pi composite output]</ref> | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 6 April 2012
The Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer developed in the UK by the Raspberry Pi Foundation.
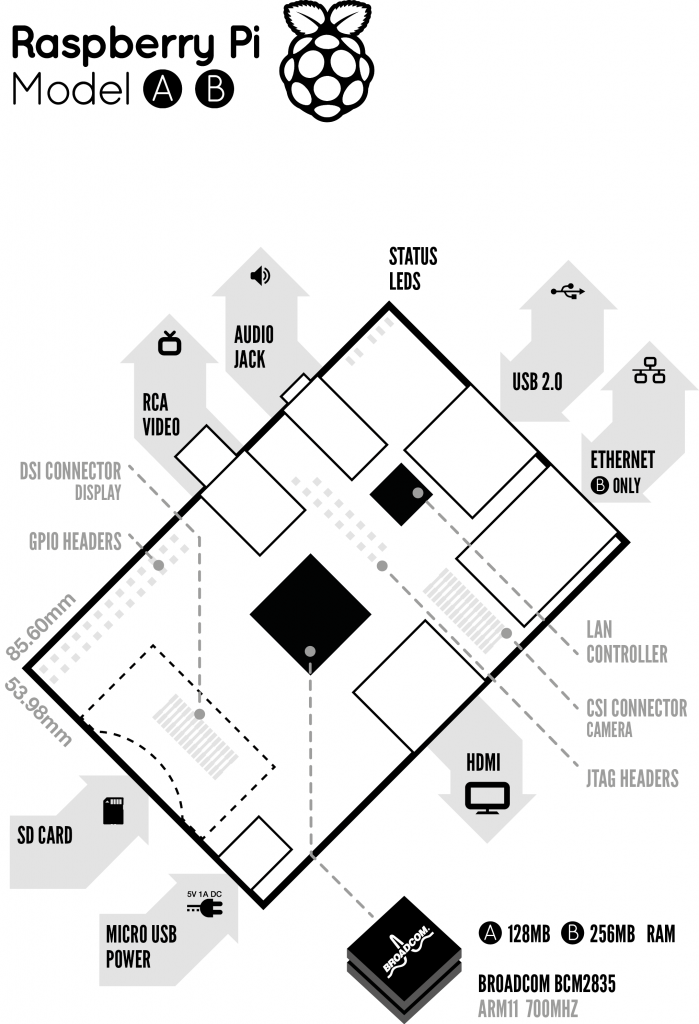
The design is based around a Broadcom BCM2835 SoC, which includes an ARM1176JZF-S 700 MHz processor, VideoCore IV GPU, and 256 MB of RAM. The design does not include internal memory, instead relying on an SD card for booting and long-term storage.
XBMC for Raspberry Pi
Team-XBMC developers are working on porting XBMC to the Raspberry Pi using beta boards supplied by the RPi Foundation.
- Raspberrypi.org- XBMC running on Raspberry Pi
- Video of XBMC running on Raspberry Pi
- XBMC.org forum thread on RPi
- Raspbmc - XBMC-centric linux-based OS install
- OpenELEC - XBMC-centric linux-based OS install
Specifications
| Model A | Model B | |
|---|---|---|
| Target price:[1] | $25 | $35[2] |
| SoC:[1] | Broadcom BCM2835 (CPU, GPU, DSP, and SDRAM)[3] | |
| CPU: | 700 MHz ARM1176JZF-S core (ARM11 family)[3] | |
| GPU: | Broadcom VideoCore IV,[4] OpenGL ES 2.0, 1080p30 h.264/MPEG-4 AVC high-profile decoder[3] | |
| Memory (SDRAM): | 256 Megabytes (shared with GPU) | |
| USB 2.0 ports:[5] | 1 | 2 (via integrated USB hub)[6] |
| Video outputs:[1] | Composite RCA (PAL & NTSC), HDMI (rev 1.3 & 1.4) [7], raw LCD Panels via DSI [8][9]
14 HDMI resolutions from 640×350 to 1920×1200 plus various PAL and NTSC standards.[10] | |
| Audio outputs:[1] | 3.5 mm jack, HDMI | |
| Onboard storage:[5] | SD / MMC / SDIO card slot | |
| Onboard network:[1][5] | None | 10/100 Ethernet (RJ45)[6] |
| Low-level peripherals: | 8 × GPIO, UART, I²C bus, SPI bus with two chip selects, +3.3 V, +5 V, ground[4][11] | |
| Power ratings: | 500 mA (2.5 W)[1] | 700 mA (3.5 W) |
| Power source:[1] | 5 volt via MicroUSB or GPIO header | |
| Size: | Template:Convert[12] | |
| Planned operating systems: | Debian GNU/Linux, Fedora, Arch Linux[13], RISC OS [14] | |
- Notes
- Model A and Model B are cultural references[15] to the original models of the British educational BBC Micro computer, developed by Acorn Computers, who originally developed the ARM processors (the architecture of the Raspberry Pi) and operating system RISC OS, which will also be able to be run on the Raspberry Pi (version 5.17).[14]
- On the model B beta boards, 128 MB was allocated by default to the GPU, leaving 128 MB for the CPU.[16] On the release model B (and Model A) three different splits are possible: 192 MB (CPU RAM) is the default split. It should be sufficent for standalone 1080p video decoding, or simple 3D (but probably not both together). 224 MB is for Linux only, with just a 1080p framebuffer; likely to fail for any video or 3D. 128 MB is for heavy 3D, possibly also with video decoding (e.g. XBMC).[17] Comparatively the Nokia 701 uses 128 MB for the Broadcom VideoCore IV.[18]
- Level 2 Cache is 128 KB, used primarily by the GPU, not the CPU.
- The ARM11 is based on version 6 of the ARM architecture, which due to its age is no longer supported by several popular versions of Linux, including Ubuntu.
- The available memory, 128–224 MiB, after subtracting 32–128 MiB for graphics memory, is less than the stated minimum requirement of 768 MiB to run a standard build of the Fedora operating system.[19] Neither the memory nor processing power meets the Debian recommended minimums, even for systems without a desktop. However, 128 MiB meets the absolute minimum for an i386 system, even with a desktop. The Debian manual states: "most users risk being frustrated if they ignore these suggestions."[20]
- The 128–224 MiB of available memory is twice the minimum requirement of 64 MiB needed to run Slackware Linux on an ARM or i386 system.[21] There are reports of Slackware running well on 32 MB ARM[22] and i386[23] systems. (While Slackware can load and run a GUI, it was designed to be run from the shell.) The Fluxbox window manager running under X Windows requires an additional 48 MB of RAM[24] (112 MB total).
- the Raspberry Pi (model B) also contains a 15-pin MIPI Camera interface (CSI) connector, which at the moment is unsupported, but the foundation is planning to release a camera module for it, sometime in the near future.[25][26]
- Support for Raw LCD Panels is available in hardware through the available DSI connector from the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI®) Alliance. [8] Software support is being planned.
- Supported digital video resolutions are: 640x350 EGA; 640x480 VGA; 800x600 SVGA; 1024x768 XGA; 1280×720 720p HDTV; 1280x768 WXGA Variant; 1280x800 WXGA Variant; 1280x1024 SXGA; 1366x768 WXGA Variant; 1400x1050 SXGA+; 600x1200 UXGA; 1680x1050 WXGA+; 1920x1080 1080p HDTV; 1920x1200 WUXGA.[10] Also to be supported are the generation of 576i and 480i composite video signals for PAL-BGHID, PAL-M, PAL-N, NTSC and NTSC-J [27]
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedfaq - ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 BCM2835 Media Processor; Broadcom.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Verified USB Peripherals and SDHC Cards; eLinux.org
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 SMSC LAN9512 Website; smsc.com
- ↑ Embedded Linux Wiki: Hardware Basic Setup
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Raspberry Pi Wiki, section screens
- ↑ diagram of Raspberry Pi with DSI LCD connector
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Raspberry Pi, supported video resolutions
- ↑ Raspberry Pi GPIO Connector; eLinux.org
- ↑ Final PCB artwork
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedosnews risc os - ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ I have a raspberry pi beta board ama
- ↑ Raspberry Pi boot configuration text file
- ↑ Nokia 701 has a similar Broadcom GPU
- ↑ Fedora, What will I need?
- ↑ Debian Minimum Hardware Requirements (Retrieved 16 February 2012)
- ↑ The Slackware Linux Project: Installation Help
- ↑ The ARMedslack March 2010 Archive by thread
- ↑ Slackware Linux Essentials
- ↑ Desktops: KDE vs Gnome (Linux Reviews)
- ↑ camera for the CSI-2 port
- ↑ diagram of Raspberry Pi with CSI camera connector
- ↑ examples of Raspberry Pi composite output