Windows audio: Difference between revisions
>Jjd-uk No edit summary |
>Jjd-uk No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
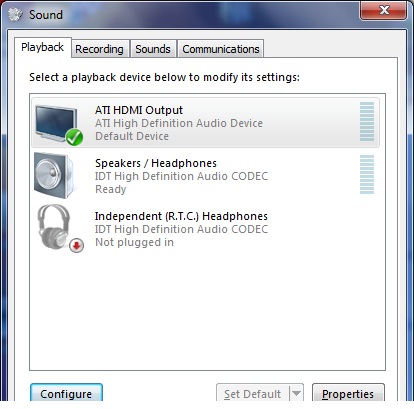
[[File:Sound - playback.jpg|800px]] | [[File:Sound - playback.jpg|800px]] | ||
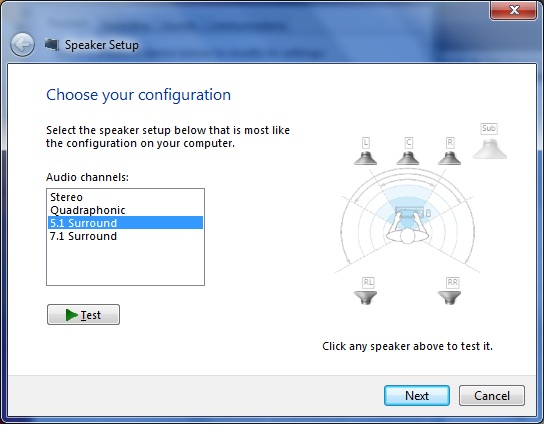
[[File:Speaker setup.jpg|800px]] | |||
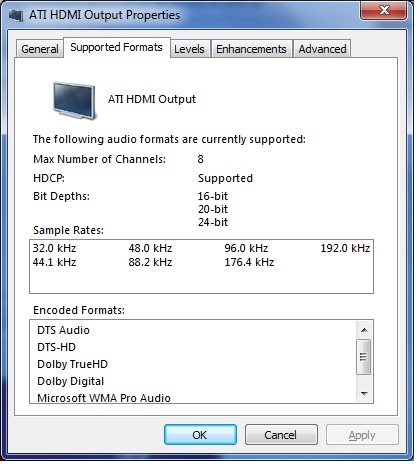
[[File:Output Properties - Supported Formats.jpg|800px]] | |||
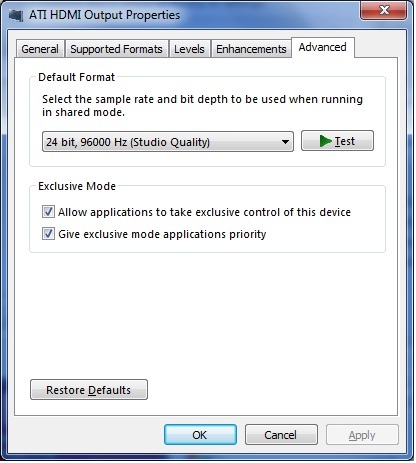
[[File:Output Properties - Advanced.jpg|800px]] | |||
Revision as of 17:59, 18 November 2012
Windows Audio API's
Since Vista SP1, Windows has two primary audio interfaces, DirectSound and Wasapi (Windows Audio Session Application Programming Interface). The latter was a replacement for XP's Kernal Streaming mode.
Directsound
DirectSound acts as a program-friendly middle layer between the program and the audio driver, which in turn speaks to the audio hardware. With DS, Windows controls the sample rate, channel layout and other details of the audio stream. Every program using sound passes it's data to DS, which then resamples as required so it can mix audio streams from any program together with system sounds.
The advantages are that programs don't need resampling code or other complexities, and any program can play sounds at the same time as others, or the same time as system sounds, because they are all mixed to one format. The disadvantages are that other programs can play at the same time, and that a program's output gets mixed to whatever the system's settings are. This means the program cannnot control the sampling rate, channel count, format, etc. Even more important for this thread is that you cannot pass through encoded formats, as DS will not decode them and it would otherwise bit-mangle them, and there is a loss of sonic quality involved in the mixing and resampling.
WASAPI
Partly to allow for cleaner, uncompromised or encoded audio, and for low-latency requirements like mixing and recording, MS re-vamped their Kernal Streaming mode after XP and came up with WASAPI for Vista.
WASAPI itself has two modes, shared and exclusive.
Shared mode is in many ways similar to DS and is not supported on XBMC so won't be covered here.
WASAPI exclusive mode bypasses the mixing/resampling layers of DS, so is passed-through as-is, and allows the application to negotiate capabilities directly with the audio driver as the format the audio data is presented in must be compatible as there is no DS between to convert it, this is why encoded formats like DTS can reach the receiver unchanged for decoding there. This negotiation often involves some back-and-forth depending on the format specified and the device's capabilities, once a format is agreed upon, the application decides how it will present the data stream.
Since WASAPI performs no mixing or resampling, it is best used in the exclusive mode and this is what XBMC uses, and as a result the application gets the exclusive rights to the audio buffers, to the exclusion of all other sounds or players. WASAPI shared mode does allow this, but that's not a common mode and not what we want for an HTPC.
In addition to Shared and Exclusive modes, there are two modes for how data is passed from the application to the audio driver.
The normal manner is in push mode - a buffer is created which the audio device draws from, and the application pushes as much data in as it can to keep that buffer full. To do this it must constantly monitor the levels in the buffer, with short "sleeps" in between to allow other threads to run.
WASAPI, and most modern sound devices, also support a "pull" or "event-driven" mode. In this mode two buffers are used. The application gives the audio driver a call-back address or function, fills one buffer and starts playback, then goes off to do other processing. It can forget about the data stream for a while. Whenever one of the two buffers is empty, the audio driver "calls you back", and gives you the address of the empty buffer. You fill this and go your way again. Between the two buffers there is a ping-pong action: one is in use and draining, the other is full and ready. As soon as the first is emptied the buffers are switched, and you are called upon to fill the empty one. So audio data is being "pulled" from the application by the audio driver, as opposed to "pushed" by the application.
WASAPI on XBMC only uses the more modern "pull" or "event-driven" mode, thus the audio hardware and drivers must be compatible with event mode is WASAPI is to be used.