Archive:HOW-TO:Install XBMC on Ubuntu/HOW-TO 3: Difference between revisions
>L.capriotti |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (354 intermediate revisions by 37 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{outdated}} | |||
Most of XBMC users are aware that '''XBMC Live''' is being released regularly by TeamXBMC, allowing a set-top box experience both running from a CD, a flash disk or fixed disk drive. '''XBMC Live''' is a streamlined Ubuntu-based system, optimized for removable media, that once installed on a fixed disk drive is a pure Ubuntu-based system, although customized for set-top box experience. | |||
An '''XBMC Live''' system will be exactly like the one that this procedure will generate, except that no build environment will be available by default. Instructions for installing a build environment are XBMCbuntu#Install XBMC unstable build environment|under "Optional Installs". | |||
This guide describes how to build an Ubuntu-based system with the minimal set of features that are part of '''XBMC Live''', from which an expert user could start to create his/her perfect setup. The result will be a customized media center allowing the user to add support for specific hardware or providing additional functionalities. Internet access is required during the installation. | |||
Although this guide is not written for Linux neophytes, it is easily followed by anyone who can complete a Linux install. | |||
This guide assumes you are using the ''Ubuntu 10.04 "Lucid Lynx" Minimal CD''. A window manager is not required for running XBMC. | |||
If your processor supports 64-bit, it is recommended you use that version of Ubuntu. Otherwise, use the 32-bit version. | |||
<div class="toclimit-3"> | |||
==Install minimal Ubuntu== | |||
The Ubuntu community provides a handy "Minimal CD image", a tiny bootable CD (<15 MB) to be used to perform a custom installation with a text-based installer. Get the most recent Lucid Lynx ISO image from [https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Installation/MinimalCD here]. | |||
* The ISO can either be burned to CD (seems like a waste for 12.5 MB); alternatively, I used [http://unetbootin.sourceforge.net/ UNetbootin] to make a bootable USB drive from ISO. | |||
After starting the computer with either the CD or the USB drive, select "Install" at boot prompt, then when prompted provide info about your location, language, keyboard layout, time zone. Disk partitioning will be basic, the full disk will be deleted and used. | |||
* Note: If you want more control on the install options you can opt for the "Expert install" at boot prompt, that provides you more flexible disk selection and partitioning options. | |||
When prompted, create an username for your account. Note that XBMC will run on its own account "xbmc" that will be created later in the install process. | |||
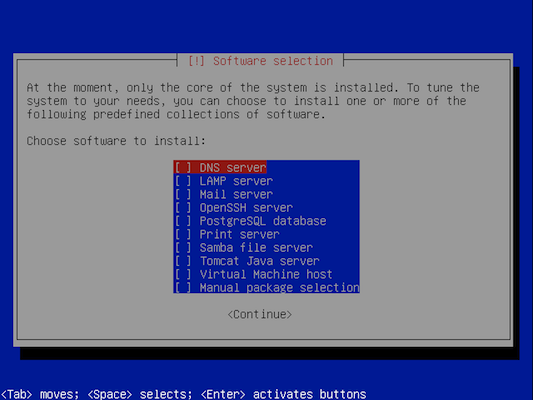
During the installation select "OpenSSH server" as the only option if you want to have (secure) remote connections facilities. | |||
[[Image:BasicUbuntu.png]] | |||
The installer will then download all the required packages and finally the system will reboot. If you installed from USB, you may be greeted with a blank screen with a single blinking cursor on reboot. This is because the installer has mistakenly installed grub on the USB drive instead of your HDD. To fix this, select the USB drive as boot drive on reboot - this will correctly launch Ubuntu. Log in with the username/password you created, and run the following to install grub on your real HDD: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo grub-install /dev/sda (replace 'a' with whatever HDD you want to boot from) | |||
sudo update-grub | |||
sudo reboot | |||
</source> | |||
On reboot you should be correctly booting from HDD. | |||
From now on, if you installed OpenSSH, you can SSH from a computer to simplify the rest of the install. | |||
==Initial system configuration== | |||
'''Note:''' You find newer XBMC packages on this [http://www.loggn.de/ubuntu-xbmc-repository-11-eden-airplay-pvr-livetv/ Repository-Overview] for Ubuntu 12.04 and older. | |||
On '''Ubuntu 9.10 or higher''', run the following commands: | |||
Stable Repository: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties pkg-config | |||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/ppa | |||
sudo apt-get update | |||
</source> | |||
Alternatively, you can follow the Unstable Repository: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties pkg-config | |||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:team-xbmc/unstable | |||
sudo apt-get update | |||
</source> | |||
==Install XBMC== | |||
The core XBMC application and its related dependencies can be installed by typing: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install xbmc xorg | |||
</source> | |||
This will take a considerable amount of time since lots of packages are due to be installed. | |||
==Install "restricted drivers" if you have an NVIDIA or ATI/AMD GPU== | |||
XBMC requires a 3D GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) that at least supports Shader Model 3.0 and OpenGL 2.0 (that features 24bpp or 32bpp for 3D hardware-acceleration support). As of writing, only Intel, ATI/AMD and NVIDIA have compatible products. However, while Intel drivers are included by default in the standard Ubuntu kernel, NVIDIA and ATI/AMD are not and require additional steps for installation. | |||
===If using NVIDIA: install NVIDIA restricted drivers=== | |||
====Method 1: Default NVIDIA drivers Installation==== | |||
Ubuntu has official packages for NVIDIA drivers in their repository. You can see these by: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
apt-cache search nvidia | grep glx | |||
</source> | |||
Looking at the listed versions from the command above enter the following command substituting 185 if you desire a different version: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install nvidia-glx-185 nvidia-settings mesa-utils libvdpau-dev | |||
</source> | |||
====Method 2: Manual Installation==== | |||
First, download the open source NVIDIA nForce drivers from [http://www.nvidia.com/object/unix.html here]. | |||
Latest version available to download is 270.41.06 for both 32-bit and 64-bit platform. This version is okay for audio over HDMI. | |||
binutils and gcc must be installed for nVidia package installer to run/compile. The installer will stop running if those packages are not found on the system. | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install binutils gcc | |||
</source> | |||
The driver can be downloaded directly using 'wget' (you may have to install wget, if not installed yet). | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install wget | |||
</source> | |||
Linux IA32 (32 bit version): | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
wget http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86/270.41.06/NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run | |||
chmod 755 NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run | |||
sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run | |||
</source> | |||
< | Linux AMD64/EM64T (64-bit version): | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
wget http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/270.41.06/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run | |||
</ | chmod 755 NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run | ||
sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run | |||
</source> | |||
If everything goes right, you should see the driver being installed on the screen. For further reading on this, look [http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=1467074 here] | |||
====Generate an xorg.conf file==== | |||
=====Default xorg.conf===== | |||
You need a proper xorg.conf file; you can generate a new one automatically by using: | |||
< | <source lang="bash"> | ||
</ | sudo nvidia-xconfig -s --no-logo --force-generate --output-xconfig=/etc/X11/xorg.conf | ||
</source> | |||
= | =====Judder free playback (NVidia Only) Very Recommended===== | ||
For a judder free playback at 23.97/59.94 Hz follow [http://forum.xbmc.org/showpost.php?p=506251&postcount=1 this guide]. | |||
====Load the NVIDIA kernel module==== | |||
The NVIDIA module can now either be loaded: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo modprobe nvidia | |||
</source> | |||
Or you can reboot and it will be automatically loaded: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo reboot | |||
</source> | |||
===If using ATI/AMD; install ATI/AMD restricted drivers=== | |||
Follow one of the two methods described in the [http://wiki.cchtml.com/index.php/Ubuntu_Lucid_Installation_Guide "Unofficial ATI Linux Driver wiki"]. | |||
Manual install is very likely to give the best results. | |||
==Install XBMC-live and Test XBMC== | |||
You do not need a window manager to run XBMC. In fact, your system will be much more lightweight without one. Instead, install the XBMC-live startup script. | |||
The xbmc-live package requires the "xbmc" account, but does not create one. Create one before you install it: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo adduser xbmc --gecos XBMC | |||
</source> | |||
Set the password to whatever you wish. | |||
< | Add the xmbc user to the required groups: | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo usermod --group adm,sudo,cdrom,floppy,audio,video,plugdev,netdev,powerdev,fuse,polkituser xbmc | |||
</ | </source> | ||
Install XBMC-live for Automated startup: | |||
(When install the unstable release use the [http://forum.xbmc.org/showpost.php?p=793399&postcount=12 link for automated startup]) | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install xbmc-live | |||
</source> | |||
Now to test, logout of your administrative user and log back in as "xbmc". Then run: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
xinit xbmc-standalone | |||
</source> | |||
If everything has been setup correctly, you should be greeted by the XBMC interface. If not, a likely culprit is your X setup. Check the logfile '''/var/log/Xorg.0.log'''. A quick way to find fatal errors is with the command: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
grep EE /var/log/Xorg.0.log | |||
</source> | |||
If you find problems, try reinstalling your drivers and editing your '''/etc/X11/xorg.conf''' file. | |||
=== Safe Mode === | |||
If you want to boot to a console for repair without starting XBMC, hold down the shift key when booting and "grub" will give you a choice of "(recovery mode)". Select this and the system will boot to a console. Alternately, you can attach a keyboard and switch out of XBMC to a text console by pressing '''CTRL-ALT-F1''' through '''CTRL-ALT-F6''', you can switch back to XBMC with '''CTRL-ALT-F7'''. | |||
== | ==Install ALSA== | ||
= | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo apt-get install alsa-utils pulseaudio | |||
</source> | |||
The sound level may be set to zero, to change the volumes we need to enter the sound mixer. | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo alsamixer | |||
</source> | |||
Adjust the channels you are interested in. | |||
Press ESC to exit out of the mixer. | |||
Save the volumes of Alsamixer. | |||
< | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo | sudo alsactl store 0 | ||
</ | </source> | ||
=== | ===Updating ALSA=== | ||
'''NOTE: Only if you experience difficulties with audio.''' | |||
There are a few issues with the current ALSA package shipped with Ubuntu, therefore it might be a good idea to upgrade. | |||
By using [http://ubuntuforums.org/showpost.php?p=10427675&postcount=1 this guide]. | |||
Credits for the script: Soundcheck/Temüjin on Ubuntu forums | |||
This should download and update your ALSA to the latest version (1.0.24.2 when writing this) | |||
*'''NOTE:''' ALSA v1.0.22.1 is installed by default with Ubuntu 10.04 [Lucid Lynx] and there is no need to upgrade if you really have some serious issues. If you have GeForce/nForce iGPU, then you can follow HOW-TO set up audio over HDMI on nVidia GeForce/nForce controller|this guide to enable audio over HDMI. | |||
Reboot the computer and check that ALSA is updated, start alsamixer and look in the caption, the version should show there. | |||
By default the sound card will have several channels muted, others with low volumes. You have to find your setup by running | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
< | alsamixer | ||
</ | </source> | ||
and adjust the channels you are interested in. | |||
Once done, save the sound volumes permanently with | |||
< | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo alsactl store 0 | |||
</source> | |||
====Updating ALSA with PPA==== | |||
By following [http://www.webupd8.org/2010/01/upgrade-to-alsa-1022-and-more-in-ubuntu.html this guide] you can update alsa with a ppa. | |||
====HDMI audio on NVidia GeForce G2xx==== | |||
By following HOW-TO set up HDMI audio on nVidia GeForce G210, GT220, or GT240|this guide you can setup HDMI audio for NVidia GT2xx | |||
====Audio over HDMI for NVidia GeForce/nForce controller==== | |||
By following HOW-TO set up audio over HDMI on nVidia GeForce/nForce controller|this guide you can setup audio over HDMI audio for NVidia GeForce/nForce. | |||
==Optional Installs== | |||
=== Install XBMC unstable build environment === | |||
If you want to walk on the bleeding edge and follow daily development of XBMC you have to install unstable and all XBMC build dependencies: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo stop xbmc-live | |||
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/team-xbmc* | |||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/unstable | |||
sudo apt-get update | |||
sudo apt-get upgrade | |||
sudo start xbmc-live | |||
</source> | |||
=== Enable the XBMC user to shutdown or put the computer to sleep === | |||
The following commands, gives the xbmc user rights to suspend, hibernate, reboot and shutdown: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install upower acpi-support | |||
</source> | |||
Create a custom-actions.pkla file with the following contents: | |||
== | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo nano /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/custom-actions.pkla | |||
</source> | |||
Put this in the file. | |||
<pre> | |||
[Actions for xbmc user] | |||
Identity=unix-user:xbmc | |||
Action=org.freedesktop.upower.*;org.freedesktop.consolekit.system.*;org.freedesktop.udisks.* | |||
ResultAny=yes | |||
ResultInactive=no | |||
ResultActive=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
For more info see this page [[Archive:Suspend and wake in Ubuntu]] | |||
===USB Automount=== | |||
To enable automount of usb mass storage (show up as source) | |||
in xbmc and to unmount (using the context menu) | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install udisks usbmount | |||
</source> | |||
< | Add NTFS support (maybe allready installed) | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install ntfs-3g | |||
</source> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo nano /etc/usbmount/usbmount.conf | |||
</source> | |||
Change line | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
FILESYSTEMS="vfat ext2 ext3 ext4 hfsplus" | |||
</source> | |||
to | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
FILESYSTEMS="ntfs vfat ext2 ext3 ext4 hfsplus" | |||
</source> | |||
Set permissions for user xbmc to handle udisks polices: | |||
Modify the file (see also previous chapter ! ): | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo nano /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/custom-actions.pkla | |||
</source> | |||
Put this in the file: | |||
<pre> | |||
[Actions for xbmc user] | |||
Identity=unix-user:xbmc | |||
Action=org.freedesktop.upower.*;org.freedesktop.consolekit.system.*;org.freedesktop.udisks.* | |||
ResultAny=yes | |||
ResultInactive=no | |||
ResultActive=yes | |||
</pre> | |||
===Custom Boot Splash=== | |||
If you want to replace the standard Ubuntu boot screen with a custom, XBMC related one TeamXBMC provides the following in its repository. | |||
To install the logo, type the following: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install plymouth-label v86d | |||
sudo wget http://excyle.nl/plymouth-theme-xbmc-logo.deb | |||
sudo dpkg -i plymouth-theme-xbmc-logo.deb | |||
</source> | |||
Determine what resolution you want Plymouth to open at. Some common ones are '''1920x1080-24''' (1080p), '''1280x720-24''' (720p), and '''1366x768-24'''. Use this resolution in the files below. | |||
= | Change the Grub-config | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo nano /etc/default/grub | |||
</source> | |||
Add next line to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT and GRUB_GFXMODE line. If you have other arguments in your GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT, incorporate them as needed. | |||
<pre> | |||
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash video=uvesafb:mode_option=1920x1080-24,mtrr=3,scroll=ywrap" | |||
GRUB_GFXMODE=1920x1080 | |||
</pre> | |||
Change the Initramfs-Module | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo nano /etc/initramfs-tools/modules | |||
</source> | |||
Put this in the file as last line: | |||
<pre> | |||
uvesafb mode_option=1920x1080-24 mtrr=3 scroll=ywrap | |||
</pre> | |||
< | <source lang="bash"> | ||
sudo nano /etc/initramfs-tools/conf.d/splash | |||
</source> | |||
Put this in the file: | |||
<pre> | |||
FRAMEBUFFER=y | |||
</pre> | |||
If you have an NVIDIA GPU, you may run into trouble with grub doing a proper handoff. Run this sed command: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo sed -i 's/ \\$vt_handoff//g' /etc/grub.d/10_linux | |||
</source> | |||
Update grub and the initramfs. | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo update-grub | |||
sudo update-initramfs -u | |||
</source> | |||
< | Reboot | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo reboot | |||
</source> | |||
Credits to eXcyle for creating the logo and to [.A.C.I.D.] for making a tutorial. | |||
=== Support for a Remote === | |||
==== Install Lirc ==== | |||
If you prefer to navigate in XBMC with a remote, check if your remote is supported by "lirc" on their [http://www.lirc.org/ website], and if it is you can install and configure it with: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo apt-get install lirc | |||
</source> | |||
For the original XBOX DVD Dongle remote, [http://forum.xbmc.org/showpost.php?p=423466&postcount=8 configuration here] | |||
==== Resume from Sleep with Remote ==== | |||
Refer to the [[Archive:Suspend_and_wake_in_Ubuntu#Remote_Suspend_.2F_Wake|"Remote Suspend & Wake"]] section of "Ubuntu Suspend / Wake". | |||
= | ===Support for DVD=== | ||
==== Dvd-rom spin-down ==== | |||
Dvd spin-down is used, eliminating the noise of a rotating disk. | |||
[http://forum.xbmc.org/showpost.php?p=523814&postcount=1 How-to for spindown] | |||
==== Unlock the DVD/CD drive for eject ==== | |||
The eject function in XBMC may not work unless you do the following. | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo bash -c "echo dev.cdrom.lock=0 >>/etc/sysctl.conf" | |||
sudo sysctl dev.cdrom.lock=0 | |||
</source> | |||
==== Disable HAL DVD automounting ==== | |||
If you see a pop-up about the DVD device being mounted and a complaint about unsafe removal when you eject the DVD, you should disable HAL's polling for DVD insertion. Automounting through HAL is not required for DVD playback. | |||
Create a file named "/etc/hal/fdi/policy/nodvdmount.fdi" with the following contents: | |||
<source lang="xml"> | |||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> | |||
< | <deviceinfo version="0.2"> | ||
<device> | |||
<match key="storage.cdrom.dvd" bool="true"> | |||
<remove key="info.addons" type="strlist">hald-addon-storage</remove> | |||
</match> | |||
</device> | |||
</deviceinfo> | |||
</source> | |||
== Centralize Your XBMC Library, Metadata and Thumbnails == | |||
Synchronize Multiple XBMCs|Synchronize Multiple XBMC installations with MySQL | |||
= | Sharing Metadata and Thumbnails see step 3 of | ||
[http://lime-technology.com/forum/index.php?topic=11473.0 Hernandito: Sharing Metadata and Thumbnails] | |||
== Known Issues == | |||
=== Video Related === | |||
==== NVIDIA Powermizer Feature ==== | |||
I encountered a lot of playback issues who are related to the powermizer feature of my Nettop. | |||
I solved them by adding powermizer settings to the xorg.conf after reading this page: | |||
[http://tutanhamon.com.ua/technovodstvo/NVIDIA-UNIX-driver/#power-saving See Link] | |||
= | ==== Overscan ==== | ||
When connecting the PC to the TV using HDMI, the 4 sides of the screen may be cut off. The recommended fix is to set [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pixel_mapping 1:1 pixel mapping] on your display. | |||
=== Sound Related === | |||
==== Multi-channel PCM over HDMI is broken ==== | |||
Due to a bug in the nvidia drivers version > 185, multi-channel audio (in non-passthrough mode) will be sent as regular stereo. These are the consequences: | |||
* Multi-channel audio (typically AAC which XBMC needs to decode) will come through as a normal stereo signal | |||
* Voices are muted - they are supposed to come over the center channel, which has been discarded as consequence of the stereo signal | |||
Possible workarounds: | |||
# Use nvidia driver version 185 with ALSA 1.0.21 or later, or | |||
# Use any nvidia driver version, but enable down-sampling in the audio settings - you will lose surround, but at least everything can be heard. | |||
= | <big>[[File:Attention talk.png|40px|link=http://www.nvnews.net/vbulletin/showthread.php?t=140999]] [http://www.nvnews.net/vbulletin/showthread.php?t=140999|'''Follow the discussion here''']</big> | ||
==== Sound Delay Issue ==== | |||
When using HDMI to connect the the audio of the PC to a TV, there appears to be a 2-3 second delay after the video playback is resumed before sound plays. The issues does not occur when the the analog audio out is used. More information on this issue is available at: [http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?t=59176 this thread] and [http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?t=59469 this thread]. | |||
== External Links == | |||
* [http://forum.xbmc.org/forumdisplay.php?f=52 XBMC Linux Forum] Here you can find different solutions to problems of XBMC on Linux. | |||
* [http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?tid=141369 XBMC Automated Efficient minimal install Script] I believe this is the most up to date version of the setup script. | |||
* [http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?t=69753 Complete & Easy XBMC Install script for ION Based Systems] Pretty impressive installer script. (unmaintained version use above) | |||
* [http://lifehacker.com/5391308/build-a-silent-standalone-xbmc-media-center-on-the-cheap Lifehacker article on "Build a Silent, Standalone XBMC Media Center On the Cheap"] | |||
* [http://www.xbmc.org/forum/showthread.php?t=53812 HOW-TO make a minimal install of Ubuntu on Acer Revo ION in under 25 minutes] Some of this guide is based upon the forum | |||
* [http://forum.xbmc.org/showthread.php?p=374815#post374815 XBMC Setup Script - Automatic installation of XBMC for Linux] The script was built for Ubuntu 9.04 (I believe). Some of the action performed are no longer needed. Page 18 has an updated version, but still performs actions that are not strictly required. | |||
Latest revision as of 01:00, 20 August 2020

|
THIS PAGE IS OUTDATED:
This page or section has not been updated in a long time, no longer applies, refers to features that have been replaced/removed, and/or may not be reliable. This page is only kept for historical reasons, or in case someone wants to try updating it. |
Most of XBMC users are aware that XBMC Live is being released regularly by TeamXBMC, allowing a set-top box experience both running from a CD, a flash disk or fixed disk drive. XBMC Live is a streamlined Ubuntu-based system, optimized for removable media, that once installed on a fixed disk drive is a pure Ubuntu-based system, although customized for set-top box experience.
An XBMC Live system will be exactly like the one that this procedure will generate, except that no build environment will be available by default. Instructions for installing a build environment are XBMCbuntu#Install XBMC unstable build environment|under "Optional Installs".
This guide describes how to build an Ubuntu-based system with the minimal set of features that are part of XBMC Live, from which an expert user could start to create his/her perfect setup. The result will be a customized media center allowing the user to add support for specific hardware or providing additional functionalities. Internet access is required during the installation.
Although this guide is not written for Linux neophytes, it is easily followed by anyone who can complete a Linux install.
This guide assumes you are using the Ubuntu 10.04 "Lucid Lynx" Minimal CD. A window manager is not required for running XBMC.
If your processor supports 64-bit, it is recommended you use that version of Ubuntu. Otherwise, use the 32-bit version.
Install minimal Ubuntu
The Ubuntu community provides a handy "Minimal CD image", a tiny bootable CD (<15 MB) to be used to perform a custom installation with a text-based installer. Get the most recent Lucid Lynx ISO image from here.
- The ISO can either be burned to CD (seems like a waste for 12.5 MB); alternatively, I used UNetbootin to make a bootable USB drive from ISO.
After starting the computer with either the CD or the USB drive, select "Install" at boot prompt, then when prompted provide info about your location, language, keyboard layout, time zone. Disk partitioning will be basic, the full disk will be deleted and used.
- Note: If you want more control on the install options you can opt for the "Expert install" at boot prompt, that provides you more flexible disk selection and partitioning options.
When prompted, create an username for your account. Note that XBMC will run on its own account "xbmc" that will be created later in the install process.
During the installation select "OpenSSH server" as the only option if you want to have (secure) remote connections facilities.
The installer will then download all the required packages and finally the system will reboot. If you installed from USB, you may be greeted with a blank screen with a single blinking cursor on reboot. This is because the installer has mistakenly installed grub on the USB drive instead of your HDD. To fix this, select the USB drive as boot drive on reboot - this will correctly launch Ubuntu. Log in with the username/password you created, and run the following to install grub on your real HDD:
sudo grub-install /dev/sda (replace 'a' with whatever HDD you want to boot from) sudo update-grub sudo reboot
On reboot you should be correctly booting from HDD.
From now on, if you installed OpenSSH, you can SSH from a computer to simplify the rest of the install.
Initial system configuration
Note: You find newer XBMC packages on this Repository-Overview for Ubuntu 12.04 and older.
On Ubuntu 9.10 or higher, run the following commands:
Stable Repository:
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties pkg-config sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/ppa sudo apt-get update
Alternatively, you can follow the Unstable Repository:
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties pkg-config sudo apt-add-repository ppa:team-xbmc/unstable sudo apt-get update
Install XBMC
The core XBMC application and its related dependencies can be installed by typing:
sudo apt-get install xbmc xorg
This will take a considerable amount of time since lots of packages are due to be installed.
Install "restricted drivers" if you have an NVIDIA or ATI/AMD GPU
XBMC requires a 3D GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) that at least supports Shader Model 3.0 and OpenGL 2.0 (that features 24bpp or 32bpp for 3D hardware-acceleration support). As of writing, only Intel, ATI/AMD and NVIDIA have compatible products. However, while Intel drivers are included by default in the standard Ubuntu kernel, NVIDIA and ATI/AMD are not and require additional steps for installation.
If using NVIDIA: install NVIDIA restricted drivers
Method 1: Default NVIDIA drivers Installation
Ubuntu has official packages for NVIDIA drivers in their repository. You can see these by:
apt-cache search nvidia | grep glx
Looking at the listed versions from the command above enter the following command substituting 185 if you desire a different version:
sudo apt-get install nvidia-glx-185 nvidia-settings mesa-utils libvdpau-dev
Method 2: Manual Installation
First, download the open source NVIDIA nForce drivers from here.
Latest version available to download is 270.41.06 for both 32-bit and 64-bit platform. This version is okay for audio over HDMI.
binutils and gcc must be installed for nVidia package installer to run/compile. The installer will stop running if those packages are not found on the system.
sudo apt-get install binutils gcc
The driver can be downloaded directly using 'wget' (you may have to install wget, if not installed yet).
sudo apt-get install wget
Linux IA32 (32 bit version):
wget http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86/270.41.06/NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run chmod 755 NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86-270.41.06.run
Linux AMD64/EM64T (64-bit version):
wget http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/270.41.06/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run chmod 755 NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-270.41.06.run
If everything goes right, you should see the driver being installed on the screen. For further reading on this, look here
Generate an xorg.conf file
Default xorg.conf
You need a proper xorg.conf file; you can generate a new one automatically by using:
sudo nvidia-xconfig -s --no-logo --force-generate --output-xconfig=/etc/X11/xorg.conf
Judder free playback (NVidia Only) Very Recommended
For a judder free playback at 23.97/59.94 Hz follow this guide.
Load the NVIDIA kernel module
The NVIDIA module can now either be loaded:
sudo modprobe nvidia
Or you can reboot and it will be automatically loaded:
sudo reboot
If using ATI/AMD; install ATI/AMD restricted drivers
Follow one of the two methods described in the "Unofficial ATI Linux Driver wiki". Manual install is very likely to give the best results.
Install XBMC-live and Test XBMC
You do not need a window manager to run XBMC. In fact, your system will be much more lightweight without one. Instead, install the XBMC-live startup script.
The xbmc-live package requires the "xbmc" account, but does not create one. Create one before you install it:
sudo adduser xbmc --gecos XBMC
Set the password to whatever you wish.
Add the xmbc user to the required groups:
sudo usermod --group adm,sudo,cdrom,floppy,audio,video,plugdev,netdev,powerdev,fuse,polkituser xbmc
Install XBMC-live for Automated startup: (When install the unstable release use the link for automated startup)
sudo apt-get install xbmc-live
Now to test, logout of your administrative user and log back in as "xbmc". Then run:
xinit xbmc-standalone
If everything has been setup correctly, you should be greeted by the XBMC interface. If not, a likely culprit is your X setup. Check the logfile /var/log/Xorg.0.log. A quick way to find fatal errors is with the command:
grep EE /var/log/Xorg.0.log
If you find problems, try reinstalling your drivers and editing your /etc/X11/xorg.conf file.
Safe Mode
If you want to boot to a console for repair without starting XBMC, hold down the shift key when booting and "grub" will give you a choice of "(recovery mode)". Select this and the system will boot to a console. Alternately, you can attach a keyboard and switch out of XBMC to a text console by pressing CTRL-ALT-F1 through CTRL-ALT-F6, you can switch back to XBMC with CTRL-ALT-F7.
Install ALSA
sudo apt-get install alsa-utils pulseaudio
The sound level may be set to zero, to change the volumes we need to enter the sound mixer.
sudo alsamixer
Adjust the channels you are interested in. Press ESC to exit out of the mixer.
Save the volumes of Alsamixer.
sudo alsactl store 0
Updating ALSA
NOTE: Only if you experience difficulties with audio.
There are a few issues with the current ALSA package shipped with Ubuntu, therefore it might be a good idea to upgrade.
By using this guide.
Credits for the script: Soundcheck/Temüjin on Ubuntu forums
This should download and update your ALSA to the latest version (1.0.24.2 when writing this)
- NOTE: ALSA v1.0.22.1 is installed by default with Ubuntu 10.04 [Lucid Lynx] and there is no need to upgrade if you really have some serious issues. If you have GeForce/nForce iGPU, then you can follow HOW-TO set up audio over HDMI on nVidia GeForce/nForce controller|this guide to enable audio over HDMI.
Reboot the computer and check that ALSA is updated, start alsamixer and look in the caption, the version should show there.
By default the sound card will have several channels muted, others with low volumes. You have to find your setup by running
alsamixer
and adjust the channels you are interested in. Once done, save the sound volumes permanently with
sudo alsactl store 0
Updating ALSA with PPA
By following this guide you can update alsa with a ppa.
HDMI audio on NVidia GeForce G2xx
By following HOW-TO set up HDMI audio on nVidia GeForce G210, GT220, or GT240|this guide you can setup HDMI audio for NVidia GT2xx
Audio over HDMI for NVidia GeForce/nForce controller
By following HOW-TO set up audio over HDMI on nVidia GeForce/nForce controller|this guide you can setup audio over HDMI audio for NVidia GeForce/nForce.
Optional Installs
Install XBMC unstable build environment
If you want to walk on the bleeding edge and follow daily development of XBMC you have to install unstable and all XBMC build dependencies:
sudo stop xbmc-live sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/team-xbmc* sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/unstable sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo start xbmc-live
Enable the XBMC user to shutdown or put the computer to sleep
The following commands, gives the xbmc user rights to suspend, hibernate, reboot and shutdown:
sudo apt-get install upower acpi-support
Create a custom-actions.pkla file with the following contents:
sudo nano /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/custom-actions.pkla
Put this in the file.
[Actions for xbmc user] Identity=unix-user:xbmc Action=org.freedesktop.upower.*;org.freedesktop.consolekit.system.*;org.freedesktop.udisks.* ResultAny=yes ResultInactive=no ResultActive=yes
For more info see this page Archive:Suspend and wake in Ubuntu
USB Automount
To enable automount of usb mass storage (show up as source) in xbmc and to unmount (using the context menu)
sudo apt-get install udisks usbmount
Add NTFS support (maybe allready installed)
sudo apt-get install ntfs-3g
sudo nano /etc/usbmount/usbmount.conf
Change line
FILESYSTEMS="vfat ext2 ext3 ext4 hfsplus"
to
FILESYSTEMS="ntfs vfat ext2 ext3 ext4 hfsplus"
Set permissions for user xbmc to handle udisks polices: Modify the file (see also previous chapter ! ):
sudo nano /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/custom-actions.pkla
Put this in the file:
[Actions for xbmc user] Identity=unix-user:xbmc Action=org.freedesktop.upower.*;org.freedesktop.consolekit.system.*;org.freedesktop.udisks.* ResultAny=yes ResultInactive=no ResultActive=yes
Custom Boot Splash
If you want to replace the standard Ubuntu boot screen with a custom, XBMC related one TeamXBMC provides the following in its repository.
To install the logo, type the following:
sudo apt-get install plymouth-label v86d sudo wget http://excyle.nl/plymouth-theme-xbmc-logo.deb sudo dpkg -i plymouth-theme-xbmc-logo.deb
Determine what resolution you want Plymouth to open at. Some common ones are 1920x1080-24 (1080p), 1280x720-24 (720p), and 1366x768-24. Use this resolution in the files below.
Change the Grub-config
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
Add next line to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT and GRUB_GFXMODE line. If you have other arguments in your GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT, incorporate them as needed.
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash video=uvesafb:mode_option=1920x1080-24,mtrr=3,scroll=ywrap" GRUB_GFXMODE=1920x1080
Change the Initramfs-Module
sudo nano /etc/initramfs-tools/modules
Put this in the file as last line:
uvesafb mode_option=1920x1080-24 mtrr=3 scroll=ywrap
sudo nano /etc/initramfs-tools/conf.d/splash
Put this in the file:
FRAMEBUFFER=y
If you have an NVIDIA GPU, you may run into trouble with grub doing a proper handoff. Run this sed command:
sudo sed -i 's/ \\$vt_handoff//g' /etc/grub.d/10_linux
Update grub and the initramfs.
sudo update-grub sudo update-initramfs -u
Reboot
sudo reboot
Credits to eXcyle for creating the logo and to [.A.C.I.D.] for making a tutorial.
Support for a Remote
Install Lirc
If you prefer to navigate in XBMC with a remote, check if your remote is supported by "lirc" on their website, and if it is you can install and configure it with:
sudo apt-get install lirc
For the original XBOX DVD Dongle remote, configuration here
Resume from Sleep with Remote
Refer to the "Remote Suspend & Wake" section of "Ubuntu Suspend / Wake".
Support for DVD
Dvd-rom spin-down
Dvd spin-down is used, eliminating the noise of a rotating disk. How-to for spindown
Unlock the DVD/CD drive for eject
The eject function in XBMC may not work unless you do the following.
sudo bash -c "echo dev.cdrom.lock=0 >>/etc/sysctl.conf" sudo sysctl dev.cdrom.lock=0
Disable HAL DVD automounting
If you see a pop-up about the DVD device being mounted and a complaint about unsafe removal when you eject the DVD, you should disable HAL's polling for DVD insertion. Automounting through HAL is not required for DVD playback.
Create a file named "/etc/hal/fdi/policy/nodvdmount.fdi" with the following contents:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<deviceinfo version="0.2">
<device>
<match key="storage.cdrom.dvd" bool="true">
<remove key="info.addons" type="strlist">hald-addon-storage</remove>
</match>
</device>
</deviceinfo>
Centralize Your XBMC Library, Metadata and Thumbnails
Synchronize Multiple XBMCs|Synchronize Multiple XBMC installations with MySQL
Sharing Metadata and Thumbnails see step 3 of Hernandito: Sharing Metadata and Thumbnails
Known Issues
Video Related
NVIDIA Powermizer Feature
I encountered a lot of playback issues who are related to the powermizer feature of my Nettop. I solved them by adding powermizer settings to the xorg.conf after reading this page: See Link
Overscan
When connecting the PC to the TV using HDMI, the 4 sides of the screen may be cut off. The recommended fix is to set 1:1 pixel mapping on your display.
Sound Related
Multi-channel PCM over HDMI is broken
Due to a bug in the nvidia drivers version > 185, multi-channel audio (in non-passthrough mode) will be sent as regular stereo. These are the consequences:
- Multi-channel audio (typically AAC which XBMC needs to decode) will come through as a normal stereo signal
- Voices are muted - they are supposed to come over the center channel, which has been discarded as consequence of the stereo signal
Possible workarounds:
- Use nvidia driver version 185 with ALSA 1.0.21 or later, or
- Use any nvidia driver version, but enable down-sampling in the audio settings - you will lose surround, but at least everything can be heard.
Sound Delay Issue
When using HDMI to connect the the audio of the PC to a TV, there appears to be a 2-3 second delay after the video playback is resumed before sound plays. The issues does not occur when the the analog audio out is used. More information on this issue is available at: this thread and this thread.
External Links
- XBMC Linux Forum Here you can find different solutions to problems of XBMC on Linux.
- XBMC Automated Efficient minimal install Script I believe this is the most up to date version of the setup script.
- Complete & Easy XBMC Install script for ION Based Systems Pretty impressive installer script. (unmaintained version use above)
- Lifehacker article on "Build a Silent, Standalone XBMC Media Center On the Cheap"
- HOW-TO make a minimal install of Ubuntu on Acer Revo ION in under 25 minutes Some of this guide is based upon the forum
- XBMC Setup Script - Automatic installation of XBMC for Linux The script was built for Ubuntu 9.04 (I believe). Some of the action performed are no longer needed. Page 18 has an updated version, but still performs actions that are not strictly required.